In this article, we will explain what a Gas Turbine Generator is, examine its applications and functions.
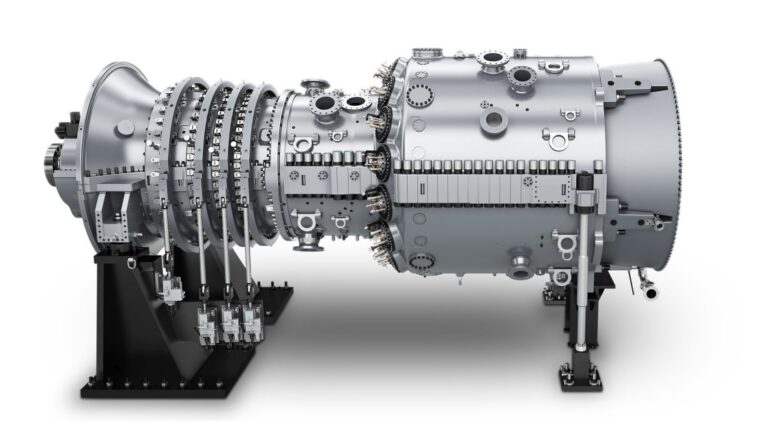
A Gas Turbine Generator is a complex machine consisting of various components that work together to produce electrical power. These components include the compressor, combustion chamber, turbine, generator, and control system.
The compressor is the first component in the gas turbine generator. It takes in air from the atmosphere and compresses it before passing it into the combustion chamber. This process increases the air pressure, which enhances the efficiency of the combustion process.
The combustion chamber is where the fuel and compressed air mix and burn. This process generates high-temperature gases that pass through the turbine blades, causing them to rotate.
The turbine is connected to the generator and converts the energy from the high-temperature gases into rotational energy. The generator then converts this rotational energy into electrical energy, which can be used for various purposes.
The control system is an essential part of the generator, responsible for monitoring and regulating the operation of the different components. It ensures that the machine operates at optimal efficiency while maintaining safe operating conditions.
In addition to these core components, gas turbine generators also have auxiliary systems such as lubrication and cooling systems, which play a critical role in ensuring the longevity of the machine.
Overall, the gas turbine generator is a sophisticated piece of machinery that requires careful engineering and maintenance to ensure its reliable operation over an extended period of time.
The Performance
the generator is designed to produce electrical power by burning fuel and converting the resulting energy into electricity. The machine’s efficiency and performance depend on several factors, including its size, speed, and load capacity.
The basic operation of a Gas Turbine Generator involves compressing air from the atmosphere and mixing it with fuel in the combustion chamber to produce high-temperature gases. The pressure generated by the combustion process causes the turbine blades to rotate, which drives the generator to produce electricity.
The efficiency of the gas turbine generator depends on several factors, such as the temperature and pressure of the gases passing through the turbine. Higher temperatures and pressures result in increased efficiency, but these conditions may also increase wear on the machine components, requiring more frequent maintenance.
To maximize the performance and lifespan of a gas turbine generator, it must be operated under optimal conditions, which include maintaining proper lubrication and cooling of the different components. Regular maintenance and cleaning of the compressor blades and turbine are also essential for optimal performance.
In addition to producing electricity, this generators can also provide mechanical power for other applications such as driving pumps and compressors. These machines are commonly used in power plants, oil and gas refineries, and industrial facilities to meet various energy needs.
Overall, gas turbine generators are highly efficient and reliable machines that play a crucial role in meeting the world’s energy demands. With proper maintenance and operation, they can operate at peak performance for many years, providing a cost-effective and sustainable source of energy.
The Application
this generators, also known as combustion turbines, are widely used in various industries for power generation. These turbines operate on the Brayton cycle, which involves compressing air, adding fuel and igniting it to produce high-pressure gas that drives a turbine. Gas turbine generators range in size from small portable units to large industrial generators capable of producing hundreds of megawatts of electricity.
One of the most common applications of gas turbine generators is in power plants. In these facilities, this generators are often used in conjunction with steam turbines to produce electricity. The gas turbine produces hot exhaust gases that are then used to generate steam, which drives a steam turbine to generate even more electricity. This combined cycle configuration can achieve efficiencies of up to 60%, making it an attractive option for large-scale power generation.
Gas turbine generators are also commonly used in the oil and gas industry to power drilling rigs, pumps, and other equipment. These generators are typically mounted on trailers or skids for ease of transport and can be quickly mobilized to remote locations. In addition, this generators are often used in offshore oil platforms where a reliable source of power is critical.
Another important application of gas turbine generators is in aviation. Turbofan engines, which are a type of gas turbine generator, power most commercial aircraft. Turbofans use a portion of the exhaust gases to drive a fan that provides additional thrust, resulting in improved fuel efficiency and reduced noise levels.
this generators are also used in the marine industry to power ships and submarines. These generators can be used to provide propulsion as well as electrical power.
Finally, gas turbine generators are often used in emergency backup power systems. Hospitals, data centers and other critical facilities often rely on this generators to provide uninterrupted power in the event of a grid outage or other emergency situation.
In conclusion, gas turbine generators are versatile and widely used in various applications across many different industries. They offer high efficiency, reliability and versatility, making them an attractive option for power generation in a variety of contexts.
We have answered the question what is gas turbine generator ? in this article and hope it has been useful for you. We appreciate you staying with us (Mehrgan Petro Pars) until the end of the article.”